
In the intricate landscape of modern finance, the process of curating personalized financial services has become increasingly sophisticated. This section delves into the mechanisms through which entities that collect and analyze vast amounts of personal information play a pivotal role in tailoring specific financial products to individual consumers. By examining the interplay between these information aggregators and the financial institutions, we can better understand the nuances of how personalized financial options are presented to the public.
Information Aggregators operate at the intersection of technology and finance, utilizing advanced algorithms and data analytics to interpret consumer behavior. These entities gather insights from various sources, including online activities, purchasing patterns, and demographic details. The resulting analysis is then used to guide financial institutions in crafting more targeted and appealing financial products. This process not only enhances the efficiency of marketing strategies but also influences the types of financial services available to consumers.
Moreover, the impact of these information aggregators extends beyond mere product customization. They contribute to the overall transparency and competitiveness of the financial market. By providing detailed consumer profiles, they enable financial institutions to make informed decisions about product offerings, pricing, and promotional strategies. This dynamic interaction ultimately shapes the consumer’s perception of financial products and the choices they make when selecting financial services.
In conclusion, the role of information aggregators in the financial sector is multifaceted and significant. Their ability to process and interpret large datasets not only facilitates more personalized financial proposals but also drives innovation and efficiency in the financial services industry. As we continue to navigate the digital age, understanding this role becomes increasingly crucial for both consumers and financial institutions alike.
Understanding Data Brokers’ Role
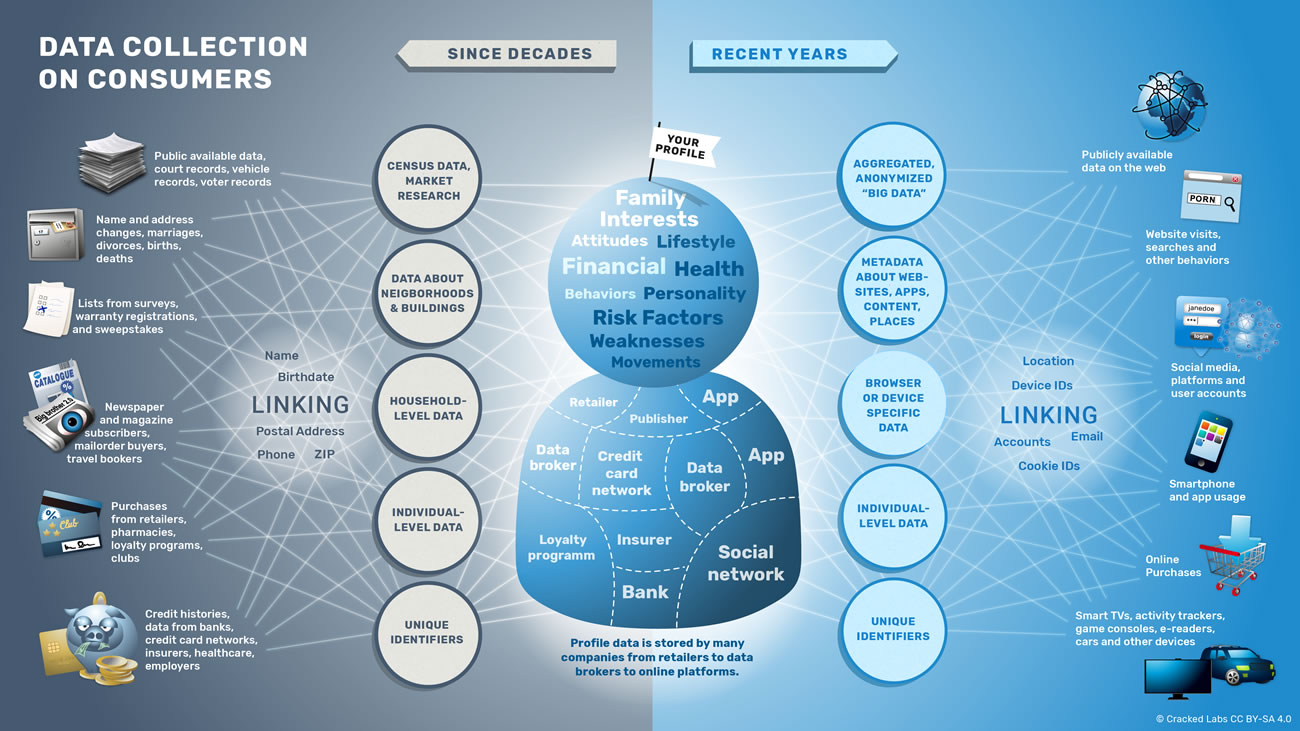
This section delves into the various techniques employed by information aggregators to gather personal details from diverse sources. It explores the mechanisms through which these entities compile and manage vast amounts of individual information, which is then utilized for various commercial purposes.
Information aggregators employ a multitude of methods to collect personal details. These techniques can be broadly categorized into two main types: How to get off BlockShopper active and passive collection methods.
- Active Collection Methods: These involve direct interactions with individuals or entities to obtain specific information. Examples include:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Information aggregators often use surveys and questionnaires to gather detailed personal information directly from individuals.
- Public Records: Accessing public records such as property deeds, court records, and professional licenses to compile personal details.
- Direct Requests: Sending direct requests to individuals for information, often through forms or online portals.
- Passive Collection Methods: These methods involve collecting information without direct interaction with individuals. Examples include:
- Web Tracking: Using cookies and other tracking technologies to monitor online activities and gather information from browsing habits.
- Data Mining: Analyzing large datasets from various sources to extract patterns and personal details.
- Third-Party Sharing: Acquiring information from third-party sources such as social media platforms, retailers, and other businesses.
Each of these methods plays a crucial role in the information aggregators’ ability to compile comprehensive profiles of individuals. Understanding these collection methods is essential for consumers to better protect their privacy and make informed decisions about sharing personal information.
Data Collection Methods Explained
This section delves into the various techniques employed by entities to gather information. Understanding these methods is crucial for individuals to comprehend the breadth of their personal information that might be collected and subsequently utilized.
Information gathering techniques are diverse and can be categorized into several key methods:
- Direct Collection: This involves gathering information directly from individuals through forms, surveys, or registrations. Common examples include online sign-ups or membership applications where users provide details voluntarily.
- Indirect Collection: Information is collected without direct interaction with the individual. This can occur through public records, social media, or other online activities that are publicly accessible.
- Third-Party Sources: Entities often obtain information from external sources such as partners, affiliates, or other organizations. This can include purchasing lists or sharing information for marketing purposes.
- Cookies and Tracking Technologies: Websites use cookies and similar technologies to track user behavior online. This includes browsing history, preferences, and other online activities, which can be aggregated to create detailed profiles.
- Data Mining: Advanced algorithms are used to analyze large datasets to extract patterns and insights. This method can uncover relationships and trends that are not immediately apparent.
Each of these methods plays a significant role in the accumulation of personal information. By understanding these practices, individuals can better protect their privacy and make informed decisions about their online activities.
How Personal Information is Sold
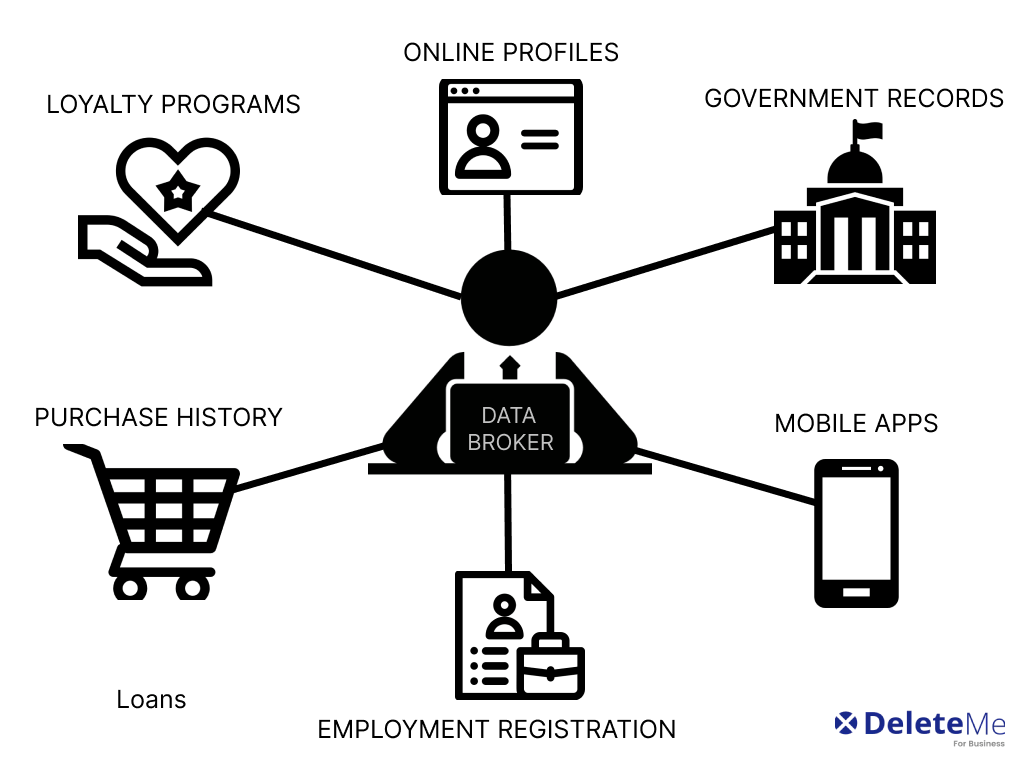
This section delves into the intricate process through which individuals’ personal details are exchanged in the marketplace. It explores the mechanisms and implications of this trade, shedding light on how these transactions can shape various aspects of consumer experiences.
Market Dynamics and Personal Information
In today’s digital economy, personal details are a valuable commodity. Companies often purchase these details from third-party sources to enhance their marketing strategies and customer targeting. This practice is widespread across industries, influencing how products and services are promoted to potential clients.
Types of Information in Demand
The types of personal details that are frequently sought after include demographic information, purchasing habits, and online behavior. These pieces of information help businesses to create more personalized marketing campaigns, which can lead to increased engagement and sales.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
While the sale of personal information is a booming industry, it is not without its controversies. There are ongoing debates about privacy rights and the ethical implications of such practices. Laws and regulations are continually evolving to protect consumers and regulate how personal information is collected, used, and sold.
Consumer Awareness and Protection
Consumers are increasingly becoming aware of the value of their personal information and are demanding more transparency and control over how it is used. Various consumer protection laws aim to empower individuals by giving them the right to know what information is being collected about them and how it is being used.
Conclusion
The sale of personal information is a complex and multifaceted issue that impacts many areas of consumer life. As technology advances and the digital landscape evolves, it is crucial for consumers to stay informed and proactive in protecting their privacy rights.
Impact on Credit Approval Rates
Understanding the role of information in the approval process is crucial for consumers and financial institutions alike. This section delves into how detailed analysis of individual profiles can significantly alter the likelihood of receiving favorable terms when applying for financial instruments.
The collection and examination of personal details play a pivotal role in determining the eligibility and conditions associated with financial products. By scrutinizing various aspects of an applicant’s financial history, institutions can make informed decisions that align with their risk management strategies.
Detailed profiling involves assessing not only credit scores but also income levels, employment stability, and previous financial behaviors. This comprehensive approach allows institutions to tailor their acceptance criteria more precisely, ensuring that the products offered are both appropriate and sustainable for the applicant.
Furthermore, this analytical process can lead to more personalized interest rates and fees, reflecting the perceived risk associated with each individual application. Those with a robust financial history and stable income sources may benefit from more favorable terms, while others might face stricter conditions or even denials based on their profile.
In conclusion, the meticulous analysis of personal financial information not only shapes the nature of financial products offered but also impacts the overall accessibility and cost of these products. It underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy financial profile and being aware of how personal information is utilized in financial assessments.
Tailoring Offers Through Data Analysis

In this section, we delve into the sophisticated methods employed by financial institutions to customize promotional deals based on comprehensive analysis of consumer information. This practice not only enhances the relevance of these deals but also aims to increase their appeal to targeted audiences.
The process begins with the collection and examination of a wide array of consumer data, ranging from purchasing habits to financial stability indicators. This information is then meticulously analyzed to identify patterns and preferences that can be leveraged to tailor specific deals. For instance, individuals with a history of frequent travel might receive promotions related to travel rewards, while those with a strong record of timely payments could be offered lower interest rates.
To illustrate this process, consider the following example. A financial institution might analyze data to find that a particular demographic frequently shops online during specific hours. By understanding this behavior, the institution can time their promotional emails to coincide with these peak shopping times, thereby increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
| Demographic | Behavior | Tailored Offer |
|---|---|---|
| Young Professionals | High spending on technology | Rewards for tech purchases |
| Frequent Travelers | Booking flights monthly | Travel points bonus |
| Homeowners | Regular home improvement purchases | Discounts on home goods |
This targeted approach not only benefits the financial institution by optimizing their marketing efforts but also provides consumers with offers that are more aligned with their needs and preferences. However, it is crucial to balance this personalization with respect for privacy and compliance with relevant regulations to ensure that consumer trust is maintained.
Consumer Protection Laws and Data Brokers
This section delves into the legal frameworks designed to safeguard individuals from the potential misuse of their personal information by entities that aggregate and trade such information. It highlights the key statutes and regulations that aim to ensure transparency, consent, and security in the handling of sensitive personal details.
Several critical laws play a pivotal role in regulating the collection, storage, and dissemination of personal information:
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This European Union legislation sets a high standard for privacy rights, requiring explicit consent for information collection and stringent data security measures.
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Similar to GDPR, this law grants California residents the right to know what information is collected about them, the right to delete it, and the right to opt-out of its sale.
- The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): This federal law regulates the use of consumer reports and ensures that such reports are accurate and used fairly in decisions such as employment and lending.
These laws not only protect consumers but also impose significant responsibilities on organizations that handle personal information. They must adhere to strict guidelines regarding data privacy and security, failure to which can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions.
Moreover, these regulations encourage transparency by mandating clear disclosures about information collection practices and the purposes for which the information is used. This helps consumers make informed decisions about their personal information and hold organizations accountable for any breaches or misuse.
In conclusion, while the collection and use of personal information by entities that aggregate such information is a powerful tool in various sectors, it is crucial that it is done within the bounds of the law. These consumer protection laws ensure that the balance between technological advancement and individual privacy rights is maintained.
Strategies to Protect Your Data Privacy
In today’s digital age, safeguarding personal information is crucial. This section outlines practical methods to enhance privacy and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive details.
One effective approach is to regularly update passwords and use strong, unique combinations for different accounts. Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that even if a password is compromised, access to the account remains protected.
Another significant strategy involves being cautious about the information shared online. Avoid posting sensitive details on social media platforms and be wary of phishing attempts that aim to extract personal information through deceptive emails or messages.
Moreover, utilizing privacy settings on digital platforms can significantly reduce the exposure of personal information. Adjusting these settings to limit who can see your profile information and posts can help maintain a higher level of privacy.
For those concerned about the collection and use of personal information by third parties, using virtual private networks (VPNs) can be beneficial. VPNs encrypt internet traffic, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to track online activities and gather personal data.
Lastly, staying informed about the latest privacy laws and regulations can empower individuals to take appropriate actions to protect their information. Understanding your rights and the protections available under the law is essential in navigating the digital landscape safely.
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Update Passwords Regularly | Change passwords frequently and use strong, unique combinations. | Prevents unauthorized access and reduces the risk of account breaches. |
| Enable Two-Factor Authentication | Add an additional verification step beyond just a password. | Enhances security by requiring a second form of identification. |
| Be Cautious with Information Sharing | Avoid posting sensitive details online and be aware of phishing attempts. | Reduces the likelihood of personal information being misused. |
| Utilize Privacy Settings | Adjust settings on digital platforms to limit information visibility. | Helps maintain privacy and control over personal information. |
| Use VPNs | Encrypt internet traffic to prevent tracking and data collection. | Provides anonymity and protects against data breaches. |
| Stay Informed About Privacy Laws | Understand legal protections and rights regarding personal information. | Empowers individuals to take appropriate actions for data protection. |
